Stomach Cancer
Overview
What is Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer, also known as gastric cancer, is the growth of abnormal cells in the lining of the stomach that forms a mass (tumour) or ulcer.
Types of Stomach Cancers
Stomach cancer is categorised based on the type of cell where the cancer originated from1:
- Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma of the stomach starts in the innermost lining of the stomach, in gland cells that produce mucus. This is the most common type of stomach cancer, accounting for 90-95% of cases2.
- Gastrointestinal stromal tumours (GIST): GIST start in very early forms of special cells in the wall of the gastrointestinal tract called the interstitial cells of Cajal. They can develop anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract, but are mostly found in the stomach and small intestine.
- Neuroendocrine tumours (NETs): NETs are cancers that begin in neuroendocrine cells (a type of cell that is like a nerve cell and a hormone-making cell) that line the gastrointestinal tract. Carcinoid tumours are a type of neuroendocrine tumour.
- Lymphoma: Lymphoma is a cancer that starts in immune cells. Lymphoma can sometimes originate in the stomach if the body sends immune cells to the stomach to fight off an infection. Most lymphomas that start in the stomach are a type of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, including mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.
In the rest of this content, stomach cancer refers mainly to adenocarcinoma of the stomach.
How Common is Stomach Cancer?
In Singapore, stomach cancer is the eighth most common cancer in men, and tenth in women. It is the sixth and seventh cause of cancer deaths in men and women, respectively. Worldwide, stomach cancer is the fifth most common cancer and fourth leading cause of cancer death4. About 75% of all new cases and deaths from stomach cancer are reported in Asia, making it a significant health challenge in this part of the world4.
The good news is that over the past fifty years, the number of stomach cancer cases has been steadily declining, due to various factors including changes in dietary patterns, improved refrigeration that led to increased availability of fresh food and less reliance on salted and preserved food, and improved public health measures to reduce Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infections4. The number of deaths from stomach cancer has also declined, particularly in countries such as Japan and South Korea which have seen an increase in early cancer detection and significantly better treatment outcomes following implementation of a national stomach cancer surveillance for their high-risk population4.
Causes & Symptoms
What causes Stomach Cancer?
Stomach cancer begins when something triggers the cells in the inner lining of the stomach to develop mutations (changes) in their DNA that cause them to grow abnormally and develop into a tumour. The exact trigger for the mutation is not fully understood yet.
Stomach Cancer Risk Factors
While the exact cause of stomach cancer remains unknown, factors that may increase the risk of stomach cancer include1,5,6:
- Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection: Chronic infection of the inner layer of the stomach with H. pylori is a major risk factor for stomach cancer, accounting for more than 60% of all cases globally4. This bacterium spreads from person to person through direct contact with saliva, vomit, or stool and is usually acquired in childhood. It can cause long term inflammation of the stomach lining, ulcers and eventually stomach cancer.
- Dietary factors: A diet high in salt, preserved, cured and smoked foods and low in fresh fruits and vegetables increases the risk of developing stomach cancer. In many developed countries, where refrigeration has allowed a greater intake of fresh rather than salt-preserved foods, rates of stomach cancer have fallen over the years.
- Alcohol: The risk for stomach cancer is strongest in people who have 3 or more drinks per day7.
- Smoking: The rate of stomach cancer is twice as high in people who smoke compared to those who are non-smokers7. Those who quit smoking lower their risk of having stomach cancer over time.
- Obesity: Carrying excess body weight increases the risk of stomach cancer, particularly cancers that develop in the upper part of the stomach.
- Environmental and occupational exposure: Workers in the rubber, metal or coal industry, and those who have been exposed to very high levels of radiation are at increased risk.
- Ethnicity: People of Asian descent have a higher risk for stomach cancer.
- Age: Stomach cancer is more common after the age of 50.
- Gender: Men are more likely to get stomach cancer compared to women.
- Chronic atrophic gastritis: This condition refers to long-term inflammation of the stomach lining which can trigger DNA mutations in the cells.
- Gastric adenomatous polyps: Adenomatous polyps, also called adenomas can sometimes develop into cancer.
- Previous stomach surgery: Stomach cancers are more likely to develop in people who have had part of their stomach removed to treat non-cancerous diseases such as ulcers.
- Family history of stomach cancer: People with one or more first degree relative(s) (parent, sibling or child) with stomach cancer have a higher likelihood of developing this disease.
- Family history of genetic syndromes: Some people inherit gene mutations (changes) that increase the risk of stomach cancer and other cancers, such as hereditary diffuse gastric cancer, Lynch syndrome, juvenile polyposis syndrome, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome and familial adenomatous polyposis. However, these inherited syndromes account for only a small percentage of stomach cancers worldwide7.
Having one or more of these risk factors does not automatically mean that you will get stomach cancer. Many people with risk factors never develop stomach cancer, whilst some with no known risk factors do.
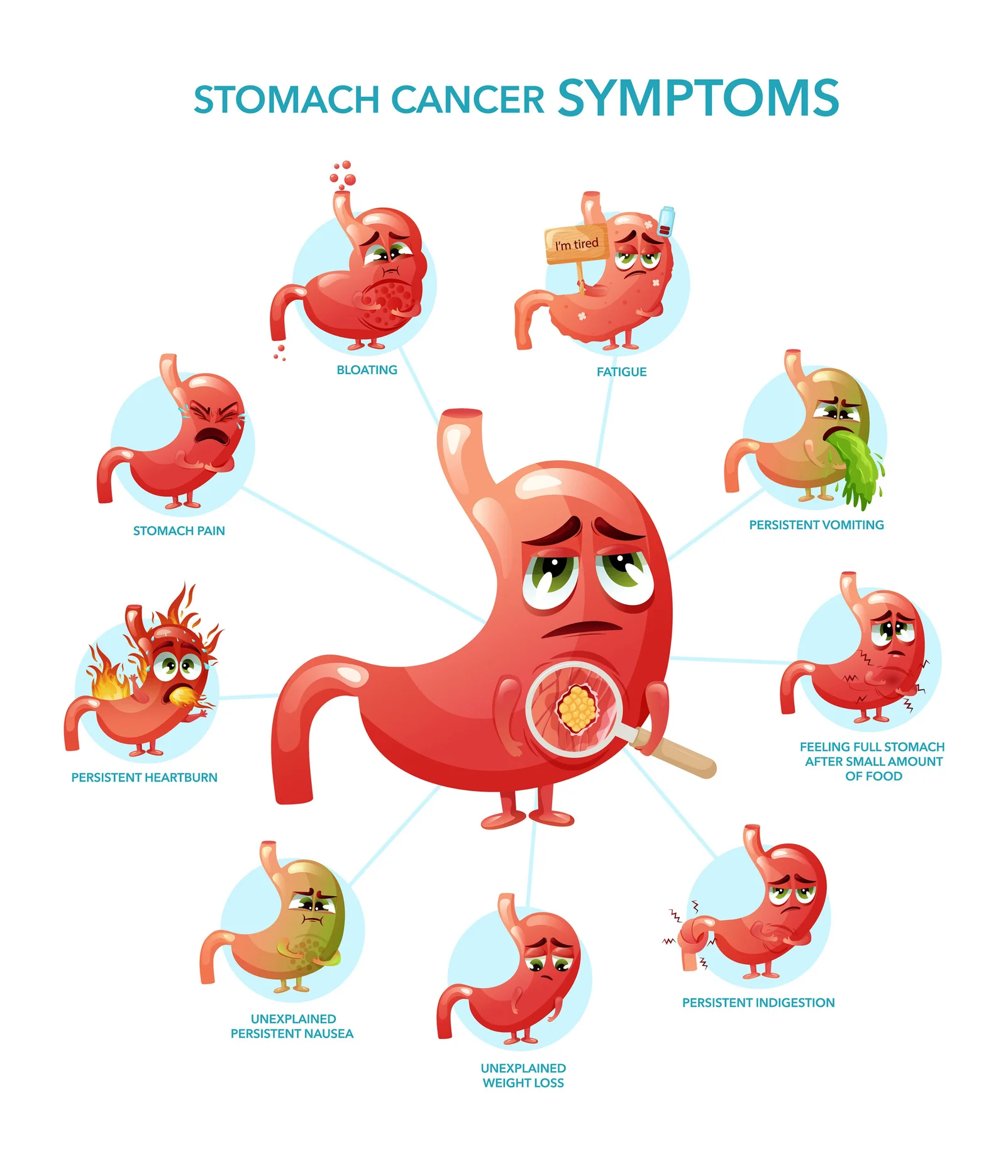
What are the Signs and Symptoms of Stomach Cancer?
This cancer has few or no symptoms in the early stages, which makes early detection difficult. When they do occur, signs and symptoms of stomach cancer may include1:
Most of these symptoms are more likely to be caused by more common ailments such as a viral infection or a stomach ulcer. However, if you have any of these symptoms, especially if they persist or get worse, you should see a doctor to have it checked out and treated if needed.
Diagnosis & Assessment
Diagnosis of Stomach Cancer
If you have symptoms or signs that suggest stomach cancer, your doctor will investigate further to determine if you have cancer. Stomach cancer can be detected through the following procedures and tests1,5,8:
- Clinical history and examination: Your doctor will ask about your personal and family medical history and perform a physical examination for masses in your abdomen.
- Blood tests: Blood tests to check your general health including your kidney and liver function will be done. Sometimes a specialised blood test to look for components of cancer cells in the blood, called circulating tumour DNA may be done if advanced cancer is suspected but a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis cannot be obtained. Tests on the cancer cell DNA can help in treatment planning.
- Gastroscopy (upper endoscopy): Stomach cancer is most often diagnosed with gastroscopy. During this procedure, the doctor puts an endoscope (a long flexible tube with a camera and light at the end) into the mouth and down into the stomach. A biopsy (tissue sample) may be taken using instruments inserted through the endoscope if any abnormal areas are seen.
- Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS): Ultrasound is an imaging test that uses sound waves to create images. It can show how far the cancer has grown into the stomach wall. Similar to a gastroscopic procedure, an endoscope is inserted down the throat and into the stomach. A special ultrasound tool is used to generate pictures of the stomach and nearby organs and lymph nodes. A biopsy of any suspicious areas may also be done under ultrasound guidance.
- Barium meal x-ray: This test involves swallowing a liquid contrast (barium) to coat the inner lining of the oesophagus, stomach, and first part of the small intestine followed by x-ray imaging. It is used less often than gastroscopy to look for stomach cancer or other stomach problems, as it can miss some abnormal areas, and it cannot take biopsy samples. But it is less invasive than endoscopy, and may be useful in certain situations.
- Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): CT or MRI scans of the abdomen may be done to visualise the three-dimensional picture of the stomach and surrounding organs. It can show the size and position of a tumour, blood vessels and whether the cancer has spread elsewhere.
- Biopsy sample testing: Samples of cancer cells obtained through biopsy is tested in the laboratory to provide further information on the type of stomach cancer it is. In addition, biomarker testing is done to look for specific genes, proteins and other substances (called biomarkers or tumour markers) that the cancer cells might have. The presence of biomarkers can guide cancer treatment selection.
How is Stomach Cancer Assessed?
After stomach cancer has been diagnosed, your doctor will determine the extent (stage) of the disease. Staging, usually done with CT scans, PET-CT scans or MRI, is done to find out whether the cancer has spread, and if so, to what parts of the body. Stomach cancer spreads most often to nearby lymph nodes and the liver. It can also go to the lining around the organs in the abdomen, which is called the peritoneum.
A staging laparoscopy may be done to determine the extent of the stomach cancer and whether removal is possible. During this surgical procedure, a few small incisions (cuts) is made in your abdomen and a long tube with a camera on the end (laparoscope) is inserted. This allows the surgeon to see inside your abdomen and look for abnormalities or signs of cancer spread. A biopsy or fluid sample from the abdomen may be taken during the procedure.
The stages of stomach cancer are5:
- Stage 0: Abnormal cells are found in the mucosa (the innermost layer of the stomach wall). These abnormal cells may become cancer and spread into nearby normal tissue. Stage 0 is also called carcinoma in situ.
- Stage I: The cancer has formed in the mucosa and may have spread to the submucosa (the second layer of the stomach wall) +/- spread to 1-2 nearby lymph nodes, or to the muscle layer.
- Stage II: The cancer has spread into the deeper walls of the stomach and to nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage III: The cancer has spread to the deepest layers of the stomach wall and nearby lymph nodes but not to other parts of the body.
- Stage IV: The cancer has spread to other parts of the body, such as the lungs, liver, distant lymph nodes, and the peritoneum (tissue that lines the abdominal wall). Stage IV is also called metastatic cancer.
- Recurrent stomach cancer: The cancer has recurred (come back) after it had been treated. Stomach cancer may come back in the stomach, lymph nodes, or other parts of the body, such as the liver, lung, or bone.
In order to facilitate treatment planning, another useful way to categorise stomach cancer is based on whether the tumour is resectable (removable by surgery) or not9:
- Very early-stage cancer: The cancer is contained in the innermost layer of the stomach wall. It has the best chance of cure with complete surgical resection (removal of the tumour).
- Potentially resectable cancer: The cancer has grown deeper into the stomach wall and may have spread into adjacent areas or lymph nodes but not to distant parts of the body. Surgery might still be possible to try to remove the cancer completely.
- Unresectable local or regional cancer: The cancer has not spread to distant parts of the body, but surgery is not possible or is too risky, for example, the cancer might be too close to vital areas, or the person might not be healthy enough for major surgery.
- Metastatic cancer: The cancer has spread to distant parts of the body and surgery will not be able to completely remove the cancer from the body.
Treatment of Stomach Cancer
Stomach Cancer Treatment Options
When considering your treatment plan your doctor will consider the following factors1,10:
- The type, size and location of the tumour.
- The stage (extent) of the disease when the cancer was found.
- Whether the tumour can be removed by surgery.
- Whether the cancer has just been diagnosed or has recurred (come back).
- Your age, overall health and any other treatments you may have for other illnesses.
- Your preferences.
Stomach cancer can be treated with the following methods, often used in combination1,11:
Surgery: This is the only effective method for curing stomach cancer. During surgery, the doctor might remove part or all of the stomach. After surgery, further treatment known as adjuvant therapy, is often recommended. This may involve chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
Surgical procedures used to treat stomach cancer include:
- Endoscopic mucosal resection: Very small Stage 0 or Stage I cancers can be cut away from the inside lining of the stomach. To remove the cancer, an endoscope is passed down the throat and into the stomach. Special cutting tools are passed through the scope to cut out the cancer.
- Subtotal (partial) gastrectomy: Only the part of the stomach affected by cancer and some of the healthy tissue around it is removed. The remaining section of stomach is then reattached to re-establish the digestive tract.
- Total gastrectomy: This procedure involves the removal of the entire stomach and surrounding tissue and other affected organs nearby. The oesophagus is then joined to the small intestine to allow food to move through the digestive system.
If the cancer has spread and cannot be removed, palliative surgery may be performed to relieve symptoms, reduce complications and improve quality of life. For example, surgery may be carried out to reduce complications of the cancer such as blockage of the stomach or bleeding from the cancer.
- Chemotherapy: Chemotherapy is the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or stop them from dividing. It can be given alone or in combination with radiotherapy after surgery. Chemotherapy is often used before surgery to treat stage 2 and stage 3 stomach cancers to help shrink the cancer for easier removal.
- Giving chemotherapy before surgery is called neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Chemotherapy might also be used after surgery if there is a risk that some cancer cells have been left behind.
- Giving chemotherapy after surgery is called adjuvant chemotherapy. Chemotherapy may also be used to reduce symptoms or prolong life in patients with advanced stomach cancer that cannot be operated upon.
- Radiation therapy (Radiotherapy): Radiotherapy uses powerful, high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. It can be used either before surgery to shrink the size of the tumour or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells, and may be combined with chemotherapy. In patients with advanced stomach cancer, radiotherapy may be useful for relieving stomach obstruction, reducing pain and stopping bleeding from cancers that cannot be operated on.
- Targeted therapy: Some stomach cancers have too much of a growth-promoting protein called HER2 on the surface of the cancer cells. Tumours with increased levels of HER2 are called HER2-positive. Trastuzumab is a man-made antibody which targets the HER2 protein. Giving trastuzumab with chemotherapy can help some patients with advanced, HER2-positive stomach cancer live longer than giving chemotherapy alone11. Another type of targeted therapy used in stomach cancer is drugs that block VEGF, which is a protein that helps tumours develop new blood vessels in order to grow. Drugs that target VEGF (or the VEGF receptors on the surface of cancer cells) can help stop some stomach cancers from growing11.
- Immunotherapy: Immunotherapy uses the body's natural defences to fight cancer by enhancing the immune system's ability to attack cancer cells. In recent years, immunotherapy drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors have been approved to treat advanced stomach cancer in some people, typically after other treatments have been tried11.
Stomach Cancer Survival Rate
Early diagnosis of stomach cancer saves lives. The earlier it is detected, the higher the likelihood for cure. Whilst more than half of stomach cancers are currently diagnosed in advanced stages (Stage III/IV), there has been an encouraging increase in the number of cases diagnosed earlier (Stage 1) over recent years13. This means that a greater proportion of people have a higher chance of being cured from stomach cancer.
It is worth noting that survival rate statistics are measured every 5 years. This means the estimate may not reflect the recent advances in stomach cancer diagnosis and treatment from the last 5 years. People who are diagnosed with stomach cancer now are likely to have a better prognosis (outcome) than these numbers show. Furthermore, breakthroughs in cancer research are happening at a faster pace than ever before, providing greater insights and leading to the development of more effective treatment options to improve the outcome and quality of life for those diagnosed with stomach cancer.
Prevention & Screening
Stomach Cancer Screening
Screening refers to looking for cancer before a person has any symptoms. The goal of screening is to detect stomach cancer early, when the cancer is localised and more likely to be cured. In countries such as Japan and South Korea where stomach cancer is much more common, a national screening programme to detect stomach cancer is used more widely. This is usually done with a yearly gastroscopy and barium x-ray. This has resulted in a greater proportion of cases being diagnosed and treated in the early stages when the chance of a cure is highest4.
In Singapore, there is currently no routine stomach cancer screening for the general population. However, a blood test, known as GASTROClear, has been developed recently by a collaborative group of researchers here in Singapore that allows the detection of early stomach cancers through a cost-effective, minimally invasive test. It measures specific microRNA (small strands of genetic material) biomarkers that are present at higher levels in the blood of stomach cancer patients, even when the cancer is in the early stages (stages I and II). In recent clinical trials, the test detected 87.5% stage I and 89.5% stage II stomach cancers14. The test report includes a stomach cancer risk score which determines if the person has a low, intermediate, or high risk of stomach cancer compared with the general population. High and intermediate-risk individuals identified through GASTROClear may then be further investigated with gastroscopy or contrast imaging.
GASTROClear is intended for adults over 40 years and at average risk of having gastric cancer with any of the following risk factors14:
- Family history of stomach cancer.
- A history of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection.
- A history of stomach lymphoma and stomach polyps.
- Long-term stomach inflammation (chronic gastritis).
- Diet containing large amounts of fried food, smoked foods, salted fish, processed meat, and pickled foods.
- Diet containing nitrites and nitrate substances commonly found in cured meats.
- Diet low in fruits and vegetables.
Stomach Cancer Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent stomach cancer, there are some measures you can take to reduce your risk1,6,15:
- Eat a healthy diet: Reduce the amount of preserved, salted, cured and smoked foods you eat. Ensure that you have plenty of fresh fruits and vegetables every day. There has been no firm scientific evidence to support the recommendation of dietary supplements or tea (particularly green tea) when it comes to lowering stomach cancer risk. Further research is needed in these areas.
- Do not smoke: Smoking increases your risk of stomach cancer and many other types of cancer. Quitting smoking can be very hard, so ask your health care provider for help.
- Stay active: Regular exercise benefits your overall health and lowers your risk for many diseases.
- Maintain a healthy body weight: Keeping to a healthy weight can help reduce your risk for many conditions, including stomach cancer.
- Go for regular screening if you are in the high-risk group.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The 5-year survival rate in Singapore for someone with stomach cancer is around 40%3. This means that 40 out of 100 people with stomach cancer are alive five years after their diagnosis. This is largely due to the fact that most stomach cancers do not show symptoms until they have progressed to an advanced stage. If diagnosed and treated early (Stage 1), the 5-year survival rate is over 80%12.
It is important to understand that these statistical numbers are obtained from a group of people with the same diagnosis to represent an average. Individuals may differ in their own experience. It is best to discuss your prognosis (outcome) with your treating doctor who would be able to provide you with more specific information based on your personal circumstances.
Most stomach cancers are not caused by inherited cancer genes, but rather by spontaneous DNA mutations (changes) acquired during a person’s lifetime. Inherited syndromes only account for a small percentage of stomach cancer worldwide.
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is a rare inherited condition with greatly increased risk of stomach cancer. This uncommon syndrome is most often caused by an inherited mutation in the CDH1 gene. It is important to identify people and families with this inherited syndrome, because most people who have it will go on to develop stomach cancer, often at a younger age15. Doctors often refer people who might have HDGC for genetic counselling. If genetic testing shows that a person has a mutation (abnormal change) in the CDH1 gene, doctors often recommend that they consider having their stomach removed before cancer develops (typically between the ages of 20 and 30)15.
Some other hereditary cancer syndromes are also linked with an increased risk for stomach cancer, including Lynch syndrome, familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP), Li-Fraumeni syndrome, and Peutz-Jeghers syndrome. Removal of the stomach is not typically recommended for people with these syndromes as their risk of stomach cancer is not nearly as high as with HDGC15. However, regular screening is recommended for this group.
Stomach cancer and its treatment can alter your relationship with food. You may have loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, mouth ulcers causing difficulty chewing and indigestion which could affect your food intake.
You might find making certain changes to your diet helpful, such as:
- Avoiding nutrient-poor foods: Where possible, choose healthy, nutrient-dense food options instead of empty calories/nutrient-poor foods such as sugary drinks, packaged snacks and carbohydrate-based desserts.
- Avoiding foods that cause indigestion: Foods such as fizzy drinks, alcohol, spicy food, pickles, citrus fruits and caffeine can cause indigestion.
- Avoiding large meals: Instead of having three larger meals, try eating six smaller meals a day, especially if you have poor appetite or if you’ve had surgery to remove part or all of your stomach.
- Having a healthy and balanced diet: A balanced diet with more fruits, vegetables and whole grains, and less preserved food, red meat and processed meats reduces the risk for cancers other than stomach cancer too.
A dietician will be able to provide you with specific recommendations if you would like more support in this area. Speak to your doctor about a referral to a dietician with an interest in cancer care.
Stomach cancer and its treatments can cause fatigue and a lack of energy. You may find that you tire a lot more easily and are unable to sustain an activity for extended periods. Allow yourself extra time to complete an activity and avoid doing too much in a day. Ensure that you have periods of rest in between. A gentle exercise programme can also help to improve your stamina. Your daily routine may also need to change to accommodate changes to your diet. For example, you may need to have frequent smaller meals instead of three main meals.
Having a cancer diagnosis can be confronting. You may experience changes in your mood such as feeling anxious, depressed or hopeless, which in turn may affect your outlook and thoughts about your future. If you find that your mood is persistently low or you are withdrawing from activities or social contact that you would previously have enjoyed, speak to your doctor.
You will also find your daily life interrupted by multiple medical appointments and hospital visits, both during and following cancer treatment. Regular follow-up will continue long-term to closely monitor your condition and detect any cancer recurrence early.
References
- Mayo Clinic. Stomach Cancer. Accessed at https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/stomach-cancer/symptoms-causes/syc-20352438 on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. What is Stomach Cancer? Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/about/what-is-stomach-cancer.html on 6 June 2024.
- National Registry of Diseases Office. Singapore Cancer Registry Annual Report 2021. Singapore, National Registry of Diseases Office; 2022.
- Ilic, M., Ilic, I. Epidemiology of Stomach Cancer. World Journal of Gastroenterology. 2022 March: 28(12): 1187–1203.
- National Cancer Institute. What is Stomach Cancer? Accessed at https://www.cancer.gov/types/stomach on 6 June 2024.
- Gleneagles Hospital Singapore. Stomach (Gastric) Cancer. Accessed at https://www.gleneagles.com.sg/conditions-diseases/stomach-cancer/symptoms-causes on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. Stomach Cancer Risk Factors. Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/risk-factors.html on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. Tests for Stomach Cancer. Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/how-diagnosed.html on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. Treatment Choices Based on the Extent of Stomach Cancer. Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/treating/by-stage.html on 6 June 2024.
- SingHealth. Stomach Cancer. Accessed at https://www.singhealth.com.sg/patient-care/conditions-treatments/stomach-cancer on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. What’s New in Stomach Cancer Research? Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/about/new-research.html on 6 June 2024.
- National Registry of Diseases Office. Singapore Cancer Registry 50th Anniversary Monograph – Appendices. Singapore, National Registry of Diseases Office; 2022.
- National Registry of Diseases Office. Singapore Cancer Registry 50th Anniversary Monograph 1968-2017. Singapore, National Registry of Diseases Office; 2022.
- Mirxes. Healthcare Professionals: Discover the GASTROClear Test. Accessed at https://gastroclear.mirxes.com/gastroclear-for-hc-professionals/ on 6 June 2024.
- American Cancer Society. Can Stomach Cancer be Prevented? Accessed at https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/stomach-cancer/causes-risks-prevention/prevention.html on 6 June 2024.
